.gif) VIARTIS
|
||
|
PARKINSON'S DISEASE |
||
|
|
||
|
|
PARKINSON'S DISEASE NEWS
|
|
|
DECEMBER 2007 back to PARKINSON'S DISEASE home page
30th December 2007 - New research PARK 7 (dj-1) - a genetic CAUSE of parkinson's disease Neuroscience Letters [2007] Dec 4; [Epub ahead of print] (Maita C, Tsuji S, Yabe I, Hamada S, Ogata A, Maita H, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Sasaki H, Ariga H.) Complete abstract DJ-1 is a gene, that when mutated is believed to be a genetic cause of Parkinson's Disease known as PARK7. For more information go to PARK 7. The function of DJ-1 is in protein formation and oxidative stress. Its loss of function is thought to be related to age of onset, mode of progression and clinical severity of both inherited and sporadic genetic forms of Parkinson's Disease. However, in this study, results showed that DJ-1 was secreted into the serum of both healthy controls and people with Parkinson's Disease. There was no significant difference between the levels of secreted DJ-1 in the two groups. There was also found to be no relationship between the amount of DJ-1 secreted, and the age of onset and clinical severity of Parkinson's Disease, and there was no relationship with the amount of oxidative stress either.
29th December 2007 - News report Most older adults have brain disease Both Parkinson's Disease and Alzheimer's Disease become progressively more common with age. Results of a brain autopsy study indicate that most older adults at the end of their life have significant brain pathology (disease), regardless of the presence or absence of outward signs of dementia.
27th December 2007 - New research trichloroethylene - new TOXIC CAUSE of parkinson's disease
Annals of Neurology [2007] Dec 21; [Epub
ahead of print] (Gash DM, Rutland K, Hudson NL, Sullivan PG, Bing G, Cass
WA, Pandya JD, Liu M, Choi DY, Hunter RL, Gerhardt GA, Smith CD, Slevin
JT, Prince TS)
Complete abstract
26th December 2007 - New research the effect of tea on parkinson's disease American journal of Epidemiology [2007] Dec 20; [Epub ahead of print] (Tan LC, Koh WP, Yuan JM, Wang R, Au WL, Tan JH, Tan EK, Yu MC.) Complete abstract A very large study assessed dietary and lifestyle factors in relation to Parkinson's disease. Just as was confirmed by previous studies, current versus never smokers exhibited a reduced risk of Parkinson's disease, and caffeine intake was inversely related to Parkinson's disease risk.
24th December 2007 - News report ADENOSINE SUBSTITUTES FOR DBS SURGERY DBS is a method of reducing symptoms that uses electrodes implanted into the brain. For more information go to Deep Brain Stimulation. It has long been debated exactly how the procedure works. Adenosine, a brain chemical most widely known as the cause of drowsiness, has now been found to be central to the effect of DBS.
22nd December 2007 - News report NEW BLOOD TEST FOR PARKINSON'S DISEASE
As part of this work
they also discovered 500 genes that are affected by Parkinson's Disease
which trigger chemical changes that can also be identified in blood
samples. DiaGenic's preliminary findings will be tested using blood
samples already collected from 300 patients. They expect to be able to
apply for a licence so that doctors could use the test by the end of next
year.
For more information go to the
Complete article.
21st December 2007 - New research Can Olfactory Testing Differentiate Parkinsonian Disorders ?
The Neurologist [2007] 13 (6) : 382-385
(McKinnon JH, Demaerschalk BM, Caviness JN, Wellik KE, Adler CH,
Wingerchuk DM.)
Complete abstract
20th December 2007 - News report KINESIA - A NEW MEANS OF ASSESSING PARKINSON'S DISEASE Cleveland Medical Devices has been awarded $1.5 million to fund further development and clinical validation of Kinesia, a quantitative motor assessment system for evaluating Parkinson's disease symptom severity. Kinesia is a compact lightweight system worn on a patient's wrist and hand. For more information go to Kinesia.
19th December 2007 - News report NEW METHOD OF DIFFERENTIATING BETWEEN PARKINSON'S DISEASE AND ESSENTIAL TREMOR
Altropane is a molecular imaging agent that binds to the dopamine transporter (DAT) protein found on the surface of dopaminergic neurons, making it visible during "SPECT" imaging. Since most forms of Parkinsonian Syndromes result in decreased activity of dopaminergic neurons, it is expected that these patients have fewer DATs than do patients without Parkinsonian Syndromes. For more information go to the Complete article. Analysis : The theory behind the use of Altropane appears to be scientifically sound. So if successful, Altropane could be of considerable benefit to the millions who have been, or will be, misdiagnosed with Parkinson's Disease. They make no mention of the f-Dopa PET scan, an existing method of physically determining Parkinson's Disease, that is little used because it is so expensive. For Altropane to be of widespread practical use it would have to be cheap enough to make it a standard procedure.
18th December 2007 - New research THE CAUSE OF FATIGUE IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE
Revista de Neurologia [2007] 45 (12) :
725-728 (Katsarou Z, Bostantjopoulou S, Hatzizisi O, Giza E, Soler-Cardona
A, Kyriazis G.)
Complete abstract
Analysis : The primary fault in Parkinson's Disease is the formation of dopamine. For more information go to Biochemistry of Parkinson's Disease. Besides affecting the muscles, dopamine stimulates the emotions. This is why the lack of dopamine that occurs in Parkinson's Disease can also cause depression. In other cell types dopamine goes on to produce noradrenaline and adrenaline. Noradrenaline and adrenaline both act as stimulants. So as somebody produces less dopamine, they will usually produce less noradrenaline and adrenaline as well, because they are both made from dopamine. So fatigue in Parkinson's Disease is not due to depression. Muscular symptoms, depression and fatigue experienced in Parkinson's Disease are all ultimately due to the same biochemical fault.
17th December 2007 - News report FAST TRACK FOR PARKINSON'S DISEASE GENE THERAPY The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted Fast Track Designation for Neurologix's experimental gene transfer procedure for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's Disease. The Neurologix procedure delivers a gene (glutamic acid decarboxylase, or GAD) to the subthalamic nucleus of the brain, where it makes an inhibitory neurotransmitter called GABA that helps to quiet the abnormal brain activity that is correlated with motor deficits characterizing Parkinson's disease.
Analysis : The approach does not address the primary fault in Parkinson's Disease, which is a lack of dopamine rather than a lack of GABA. If somebody did want to increase their GABA levels somebody could do it far more readily by taking the well established precursors and coenzyme precursors of GABA formation, which are glutamic acid and pyridoxine. Both of these nutrients are readily available and free of side effects.
15th December 2007 - New book Living Well with Parkinson's Disease Gretchen Garie, Michael J. Church, Winifred Conkling
14th December 2007 - News report CAN GREEN TEA PROTECT AGAINST PARKINSON'S DISEASE ? Researchers have suggested that the consumption of green tea, widely touted to have beneficial effects on health, can also protect brain cells. The authors investigated the effects of green tea polyphenols, a group of naturally occurring chemical substances found in plants that have antioxidant properties in an animal model of Parkinson's Disease.
13th December 2007 - New research DRUG INDUCED PARKINSONISM
Movement Disorders [2007] Dec 7; [Epub ahead
of print] (Esper CD, Factor SA.)
Complete abstract
12th December 2007 - New research LIFE EXPECTANCY IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry [2007] 78 (12) : 1304-1309 (Ishihara LS, Cheesbrough A, Brayne C, Schrag A.) Complete abstract Studies in different countries in Europe were used to assess life expectancy for people with Parkinson's Disease in comparison to normal life expectancy.
Analysis : As can be seen from the figures, Parkinson's Disease is not a fatal illness, because even in those with early onset there was a life expectancy of decades. Parkinson's Disease can reduce the ability to cope with certain medical disorders and thereby make fatality more likely. This is why some people are reported as having died of the complications of Parkinson's Disease. However, it is not indicated in the research whether this is the reason for the much lower life expectancy in Parkinson's Disease. There may be common factors that increase the likelihood of Parkinson's Disease and that quite independently lower life expectancy.
11th December 2007 - News report 24 HOUR VERSION OF REQUIP The F.D.A. (the U.S. medical authority) has approved the sale of Requip XL 24-hour�, a once-daily prolonged release reformulation of the Parkinson's Disease drug Requip. For more information go to the Complete article. Requip� is a dopamine agonist, a class of drug increasingly recommended as first-line therapy.
9th December 2007 - New research ANTI-Parkinson DRUG Mucuna pruriens shows antioxidant and chelating activity Phytotherapy Research [2007] Dec 7; [Epub ahead of print] (Dhanasekaran M, Tharakan B, Manyam BV.) Complete abstract
Researchers have shown that Mucuna Pruriens also possesses anti-oxidant qualities, which help to protect against cell damage, and also metal chelating activity, which helps to protect against excessive quantities of metals. It is suggested by the authors that the effect of Mucuna Pruriens may also be related to its antioxidant activity independent of the symptomatic effect. Analysis : When comparing Mucuna Pruriens and modern forms of L-dopa such as Sinemet, Mucuna Pruriens has other advantages. Mucuna Pruriens is milder and so greatly lessens the problem of excessive dosage that often occurs with Sinemet. Mucuna Pruriens is far more adjustable in its dosages in comparison to Sinemet, which has only two possible dosages. Besides L-dopa, Sinemet contains a substance that prevents the breakdown of L-dopa before it reaches the cells. It is claimed that Mucuna Pruriens has the equivalent, but it is not certain if this is true.
8th December 2007 - New research Complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease
Brain Research [2007] Nov 1; [Epub ahead of
print] (Parker WD Jr, Parks JK, Swerdlow RH.)
Complete abstract
Analysis : Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) needs Coenzyme Q10 in order to function properly. This may be why Coenzyme Q10 appears to have a beneficial effect in some people - because it is correcting the deficiency of Complex I that often occurs in Parkinson's Disease. However, it is not clear how this could positively affect Parkinson's Disease, because increasing energy production has no direct effect on increasing dopamine formation.
7th December 2007 - New research PARKINSON'S DISEASE RELATIVES AT HIGHER RISK OF ESSENTIAL TREMOR
Movement Disorders [2007] 22 (11) : 1607-1614 (Rocca WA, Bower JH, Ahlskog
JE, Elbaz A, Grossardt BR, McDonnell SK, Schaid DJ, Maraganore DM.)
Complete abstract
6th December 2007 - News report PARKINSON'S DISEASE RELATIVES AT HIGHER RISK OF ANXIETY AND DEPRESSION Because many patients with Parkinson's disease develop anxiety and depression after and even before the onset of the disease, researchers explored whether this tendency was present to a greater extent in family members of people with Parkinson's Disease.
5th December 2007 - History THE ROMANS TREATMENT OF TREMOR
4th December 2007 : News report
The
development of a new class of drugs
Analysis : The primary biochemical fault in Parkinson's
Disease is insufficent formation of dopamine. Even in theory, this
approach can not increase dopamine formation, and so could not rid
Parkinson's Disease. However, having exhausted all drug approaches based
on dopamine, many pharmaceutical companies are now trying very different
non-dopamine approaches. Consequently, they would eventually mean merely
adding another drug to those already being taken. 3rd December 2007 : New book Making the Connection Between Brain and Behavior : COPING WITH PARKINSON'S DISEASE Joseph H.Friedman
2nd December 2007 : New research 115 year old without any sign of dementia Neurobiology of Aging [2007] Nov 26; [Epub ahead of print] (Price JL.) Complete abstract Up to 30 % of people with Parkinson's have dementia and it is claimed that almost all patients with Parkinson's disease develop dementia over time. Rightly or wrongly, Dementia is almost seen as an inevitable part of Parkinson's Disease and growing old. The Dutch woman, Hendrikje van Andel-Schipper (1890-2005) was the oldest person in the world until her death. For more information go to Hendrijke van Andel-Schipper.
Analysis : Dementia is primarily due to a lack of acetylcholine, a substance produced in the brain. Acetylcholine is made in the brain from choline - a vitamin like substance. The richest sources of choline are eggs and oily fish (such as herrings and sardines). So her choline intake was inadvertently high, due to her daily herring consumption, enabling her to produce more acetylcholine. She also consumed daily orange juice - a rich source of vitamin C. Vitamin C is needed for Catalase, the primary enzyme required to prevent damage to the nerve cells. So rather than assuming that dementia is inevitable as people age, she is evidence that dementia can be prevented biochemically by consuming substances that the brain uses naturally in order to avoid it.
1st December 2007 : New research anger in parkinson's disease
Movement Disorders [2007] Nov 28; [Epub ahead of
print] (Macias Y, Benito-Leon J, Louis ED, Cano-Vindel A.)
Complete abstract
ARCHIVES : Current January 2009 December 2008 November 2008 October 2008 September 2008 August 2008 July 2008 June 2008 May 2008 April 2008 March 2008 February 2008 January 2008 December 2007 November 2007 October 2007 September 2007 August 2007 July 2007
|
||
|
|
||
.gif) |
||
| �2006-2007 Viartis | ||
| [email protected] | ||
 The lack of difference in the results brings in to
question whether DJ-1 is actually a genetic cause of Parkinson's Disease.
It was already known that genetic causes of Parkinson's Disease at most
normally only incline somebody to Parkinson's Disease rather than make
Parkinson's Disease inevitable.
The lack of difference in the results brings in to
question whether DJ-1 is actually a genetic cause of Parkinson's Disease.
It was already known that genetic causes of Parkinson's Disease at most
normally only incline somebody to Parkinson's Disease rather than make
Parkinson's Disease inevitable.  Only 1 in 7 older
people were free of brain disease. Most older persons with dementia had
more than one type of pathology in their brain causing the impairment.
"This most commonly was Alzheimer's disease pathology and cerebral
infarcts (strokes), followed by Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body disease,
a disease related to Parkinson's disease", the author said. "Older persons
can often handle one pathology in their brain, but the burden of more than
one pathology may tip them over the threshold of clinical dementia."
For more information go to the
Only 1 in 7 older
people were free of brain disease. Most older persons with dementia had
more than one type of pathology in their brain causing the impairment.
"This most commonly was Alzheimer's disease pathology and cerebral
infarcts (strokes), followed by Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body disease,
a disease related to Parkinson's disease", the author said. "Older persons
can often handle one pathology in their brain, but the burden of more than
one pathology may tip them over the threshold of clinical dementia."
For more information go to the
 Industrial coworkers with
Parkinson's
disease and Parkinsonism were examined who had been subjected to chronic
exposure to trichloroethylene. Workers with workstations adjacent to the
source of trichloroethylene and who were subjected to chronic inhalation
and dermal exposure from handling trichloroethylene-soaked metal parts all
had Parkinson's disease. Coworkers more distant from the trichloroethylene
source, receiving chronic respiratory exposure, displayed many features of
Parkinsonism, including significant motor slowing. Neurotoxic actions of
trichloroethylene were also demonstrated in accompanying animal studies.
Trichloroethylene joins other toxins as a risk factor for Parkinsonism.
Industrial coworkers with
Parkinson's
disease and Parkinsonism were examined who had been subjected to chronic
exposure to trichloroethylene. Workers with workstations adjacent to the
source of trichloroethylene and who were subjected to chronic inhalation
and dermal exposure from handling trichloroethylene-soaked metal parts all
had Parkinson's disease. Coworkers more distant from the trichloroethylene
source, receiving chronic respiratory exposure, displayed many features of
Parkinsonism, including significant motor slowing. Neurotoxic actions of
trichloroethylene were also demonstrated in accompanying animal studies.
Trichloroethylene joins other toxins as a risk factor for Parkinsonism.  Contrary to what is often claimed, green tea drinking was completely
unrelated to Parkinson's disease risk. However, black tea, a
caffeine-containing beverage, lowered the risk of Parkinson's disease.
Yet it was not affected by the total caffeine intake as might have been
assumed. This led the researchers to suggest that ingredients of black tea
other than caffeine appear to be responsible for the beverage's inverse
association with Parkinson's disease. However, they did not know what
these ingredients were.
Contrary to what is often claimed, green tea drinking was completely
unrelated to Parkinson's disease risk. However, black tea, a
caffeine-containing beverage, lowered the risk of Parkinson's disease.
Yet it was not affected by the total caffeine intake as might have been
assumed. This led the researchers to suggest that ingredients of black tea
other than caffeine appear to be responsible for the beverage's inverse
association with Parkinson's disease. However, they did not know what
these ingredients were. Adenosine in
the
brain is largely a byproduct of the
chemical ATP, the source of energy for all our cells. DBS causes the
release of ATP, which is then broken down into adenosine. The extra adenosine
then reduces abnormal signaling among the brain's neurons. However, even
without DBS surgery, adenosine reduced abnormal brain signaling.
The researchers have consequently suggested that it may be possible to
enhance the effect of DBS by using substances that enhance adenosine, or
to using adenosine in a way that does not even involve DBS surgical
procedure at all.
For more information go to the
Adenosine in
the
brain is largely a byproduct of the
chemical ATP, the source of energy for all our cells. DBS causes the
release of ATP, which is then broken down into adenosine. The extra adenosine
then reduces abnormal signaling among the brain's neurons. However, even
without DBS surgery, adenosine reduced abnormal brain signaling.
The researchers have consequently suggested that it may be possible to
enhance the effect of DBS by using substances that enhance adenosine, or
to using adenosine in a way that does not even involve DBS surgical
procedure at all.
For more information go to the
 A simple blood test that can diagnose
Parkinson's disease could be available from next year, according to
Diagenic.
The test could lead to earlier
diagnosis.
The research, which was funded by the
Michael J Fox Foundation, suggests that genetic alterations caused by the
condition can be detected by chemical changes in the blood. Diagenic claim
that
being able to base a diagnosis on the analysis of gene expression
signatures in sample material taken at a distance from the site of the
disease, such as peripheral blood, has clear advantages for both patients
and clinicians.
For more information go to
A simple blood test that can diagnose
Parkinson's disease could be available from next year, according to
Diagenic.
The test could lead to earlier
diagnosis.
The research, which was funded by the
Michael J Fox Foundation, suggests that genetic alterations caused by the
condition can be detected by chemical changes in the blood. Diagenic claim
that
being able to base a diagnosis on the analysis of gene expression
signatures in sample material taken at a distance from the site of the
disease, such as peripheral blood, has clear advantages for both patients
and clinicians.
For more information go to
 Each study examined different
test methods : the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test,
and "Sniffin' Sticks". The University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification
Test is moderately sensitive (77%) and specific (85%) for differentiation
of Parkinson's Disease from other Parkinsonian syndromes, but is less
specific (62%) for distinguishing Parkinson's Disease from multiple system
atrophy. Olfactory testing can differentiate between Parkinson's Disease
and other Parkinsonian disorders, but the diagnostic accuracy was not
certain enough to justify its routine clinical use.
Each study examined different
test methods : the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test,
and "Sniffin' Sticks". The University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification
Test is moderately sensitive (77%) and specific (85%) for differentiation
of Parkinson's Disease from other Parkinsonian syndromes, but is less
specific (62%) for distinguishing Parkinson's Disease from multiple system
atrophy. Olfactory testing can differentiate between Parkinson's Disease
and other Parkinsonian disorders, but the diagnostic accuracy was not
certain enough to justify its routine clinical use.  The device
monitors three-dimensional motion and
electrical muscle activity (EMG) to objectively quantify the severity of
Parkinson's disease symptoms, such as tremor, bradykinesia (slowed
movements) and dyskinesias (wild, involuntary movements). Patients follow
on screen video instruction while data is wirelessly transmitted to a
computer to enhance user safety and comfort. A previous clinical study
showed good correlation between Kinesia and the UPDRS. The UPDRS, a
subjective assessment scale, is the current standard in rating Parkinson's
symptom severity.
For more information go to the
The device
monitors three-dimensional motion and
electrical muscle activity (EMG) to objectively quantify the severity of
Parkinson's disease symptoms, such as tremor, bradykinesia (slowed
movements) and dyskinesias (wild, involuntary movements). Patients follow
on screen video instruction while data is wirelessly transmitted to a
computer to enhance user safety and comfort. A previous clinical study
showed good correlation between Kinesia and the UPDRS. The UPDRS, a
subjective assessment scale, is the current standard in rating Parkinson's
symptom severity.
For more information go to the
 Tremor disorders are diagnosed by subjective
clinical evaluation, which is associated with an error rate among general
neurologists of 25% to 35%. Consequently, hundreds of thousands of people
are being treated for Parkinson's Disease that don't actually have it, or
that have mild Parkinson's Disease and a quite separate medical
disorder that causes their tremor. Alseres
Pharmaceuticals has started phase III clinical trials of Altropane, which
is
a
new diagnostic molecular imaging agent being developed to aid in the
differentiation of Parkinsonian Syndromes from non-Parkinsonian tremor.
Tremor disorders are diagnosed by subjective
clinical evaluation, which is associated with an error rate among general
neurologists of 25% to 35%. Consequently, hundreds of thousands of people
are being treated for Parkinson's Disease that don't actually have it, or
that have mild Parkinson's Disease and a quite separate medical
disorder that causes their tremor. Alseres
Pharmaceuticals has started phase III clinical trials of Altropane, which
is
a
new diagnostic molecular imaging agent being developed to aid in the
differentiation of Parkinsonian Syndromes from non-Parkinsonian tremor.
 However, immunological factors have also been
implicated.
The purpose of this study was to assess fatigue in people with Parkinson's
Disease in relation to depression and various immunological factors.
People with Parkinson's Disease were found to suffer more from
fatigue than other people. When depression was taken account of,
immunological factors were found not to be the reason for the fatigue. It
was depression rather than immunological factors that was most related to
the cause of fatigue.
However, immunological factors have also been
implicated.
The purpose of this study was to assess fatigue in people with Parkinson's
Disease in relation to depression and various immunological factors.
People with Parkinson's Disease were found to suffer more from
fatigue than other people. When depression was taken account of,
immunological factors were found not to be the reason for the fatigue. It
was depression rather than immunological factors that was most related to
the cause of fatigue. Results
of a Phase 1 clinical study showed that the procedure was well tolerated
and resulted in improved motor function and brain metabolism for patients
with advanced Parkinson's disease over the course of the one-year study.
Neurologix is currently preparing to initiate a Phase 2 study by early
2008, subject to final FDA consent to the study protocol.
For more information go to the
Results
of a Phase 1 clinical study showed that the procedure was well tolerated
and resulted in improved motor function and brain metabolism for patients
with advanced Parkinson's disease over the course of the one-year study.
Neurologix is currently preparing to initiate a Phase 2 study by early
2008, subject to final FDA consent to the study protocol.
For more information go to the
 "Living Well with
Parkinson's Disease : What your doctor doesn't tell you...that you need to
know" is a guide to Parkinson's Disease from two people who cofounded a
national support and advocacy organization. A couple who both have
Parkinson's Disease and live daily with the effects of the disease,
discuss diagnosis, treatment options, and the emotional consequences of
this difficult illness. They deal with how Parkinson's Disease affects
relationships; and the role of diet, supplements, and rest and relaxation;
strategies for navigating professional life and the maze of the
health-care system; as well as handling everyday challenges such as
buttoning a shirt or rolling over in bed, and more.
"Living Well with
Parkinson's Disease : What your doctor doesn't tell you...that you need to
know" is a guide to Parkinson's Disease from two people who cofounded a
national support and advocacy organization. A couple who both have
Parkinson's Disease and live daily with the effects of the disease,
discuss diagnosis, treatment options, and the emotional consequences of
this difficult illness. They deal with how Parkinson's Disease affects
relationships; and the role of diet, supplements, and rest and relaxation;
strategies for navigating professional life and the maze of the
health-care system; as well as handling everyday challenges such as
buttoning a shirt or rolling over in bed, and more.
 The authors discovered that green tea
polyphenols protect dopamine neurons and that the effect increases with
the amount consumed. They claim that this protective effect is mediated by
inhibition of the ROS-NO pathway, a pathway that may contribute to cell
death in Parkinson's Disease. They hope that eventually "green tea
polyphenols may be developed into a safe and easily administrable drug for
Parkinson's disease.", and that "if green tea consumption can be shown to
have meaningful neuroprotective actions in patients, this would be an
extremely important advance."
For more information go to the
The authors discovered that green tea
polyphenols protect dopamine neurons and that the effect increases with
the amount consumed. They claim that this protective effect is mediated by
inhibition of the ROS-NO pathway, a pathway that may contribute to cell
death in Parkinson's Disease. They hope that eventually "green tea
polyphenols may be developed into a safe and easily administrable drug for
Parkinson's disease.", and that "if green tea consumption can be shown to
have meaningful neuroprotective actions in patients, this would be an
extremely important advance."
For more information go to the
 Of those cases of Drug Induced Parkinsonism,
46% were found to be caused by Atypical antipsychotics, and 29% were
caused by metoclopramide (which is sold as Reglan and various other names)
- a drug used to treat nausea and vomiting, or to facilitate gastric
emptying. Other drugs accounted for about 25% of cases of Drug Induced
Parkinsonism. These people were kept on Parkinson's Disease drugs and also
the drug that induced their symptoms. This is despite the fact that Drug
Induced Parkinsonism is reversible when the drug that causes it is ceased.
Of those cases of Drug Induced Parkinsonism,
46% were found to be caused by Atypical antipsychotics, and 29% were
caused by metoclopramide (which is sold as Reglan and various other names)
- a drug used to treat nausea and vomiting, or to facilitate gastric
emptying. Other drugs accounted for about 25% of cases of Drug Induced
Parkinsonism. These people were kept on Parkinson's Disease drugs and also
the drug that induced their symptoms. This is despite the fact that Drug
Induced Parkinsonism is reversible when the drug that causes it is ceased.
 The life expectancy was : 38 years
instead of the expected 49 years for those
whose
onset was 25-39 years old, 21 years instead of the expected 31 years for
those whose onset was 40-64 years old,
and 5 years instead of the expected 9 years for those whose onset was
after they were 64 years old.
The anticipated age of death was 71 instead of 82
for those whose onset was 25-39 years old,
and was 88 instead of 91 for those whose onset was after they were 64
years old. In summary, life expectancy was found to be much shorter in
Parkinson's Disease, regardless of the age of onset. An earlier age of
onset lessened the life expectancy even further.
The life expectancy was : 38 years
instead of the expected 49 years for those
whose
onset was 25-39 years old, 21 years instead of the expected 31 years for
those whose onset was 40-64 years old,
and 5 years instead of the expected 9 years for those whose onset was
after they were 64 years old.
The anticipated age of death was 71 instead of 82
for those whose onset was 25-39 years old,
and was 88 instead of 91 for those whose onset was after they were 64
years old. In summary, life expectancy was found to be much shorter in
Parkinson's Disease, regardless of the age of onset. An earlier age of
onset lessened the life expectancy even further.
 The new once-daily
formulation
has been developed utilizing SkyePharma's Geomatrix� prolonged release
technology. It aims at providing additional therapeutic benefits compared
with the current three times a day version of Requip, by evening out the
effect of the Requip, and simplifying the treatment regime for patients,
thus improving patient convenience and compliance. For more information go
to
The new once-daily
formulation
has been developed utilizing SkyePharma's Geomatrix� prolonged release
technology. It aims at providing additional therapeutic benefits compared
with the current three times a day version of Requip, by evening out the
effect of the Requip, and simplifying the treatment regime for patients,
thus improving patient convenience and compliance. For more information go
to
 Mucuna Pruriens is the oldest
treatment for
Parkinson's Disease.
In ancient India, as far back as 5000 B.C., they
described the symptoms of Parkinson's Disease, which they treated using
the seeds of Mucuna Pruriens. Mucuna
Pruriens
has been used continuously since then, and is presently being used
progressively more as a replacement for
L-dopa, due to the
seeds of Mucuna Pruriens being a natural source of high quantities of
L-dopa. For more information go to
Mucuna Pruriens is the oldest
treatment for
Parkinson's Disease.
In ancient India, as far back as 5000 B.C., they
described the symptoms of Parkinson's Disease, which they treated using
the seeds of Mucuna Pruriens. Mucuna
Pruriens
has been used continuously since then, and is presently being used
progressively more as a replacement for
L-dopa, due to the
seeds of Mucuna Pruriens being a natural source of high quantities of
L-dopa. For more information go to
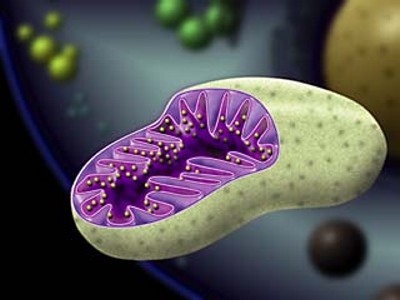 A study of Complex I activity in
Parkinson's Disease brain
has identified loss
of activity
in the substantia nigra (the part of the brain primarily affected in
Parkinson's Disease).
There were found to be increasingly
significant losses of complex I activity in Parkinson's Disease as
increasingly pure mitochondria were studied. There was little difference
in the next steps in the energy producing process (Complexes II, III, and
IV) when compared with people that did not have Parkinson's Disease.
A study of Complex I activity in
Parkinson's Disease brain
has identified loss
of activity
in the substantia nigra (the part of the brain primarily affected in
Parkinson's Disease).
There were found to be increasingly
significant losses of complex I activity in Parkinson's Disease as
increasingly pure mitochondria were studied. There was little difference
in the next steps in the energy producing process (Complexes II, III, and
IV) when compared with people that did not have Parkinson's Disease.  Immediate relatives (brother, sister, mother, father,
son or daughter) of people who have Parkinson's disease were found to at
increased risk for developing depression and anxiety disorders. The risk
is particularly increased in families
of patients who develop Parkinson's disease before age 75. The authors
emphasizes that the familial susceptibility factors may be genetic,
environmental or a combination of the two, and that further research is
needed to determine their exact nature.
For more information go to the
Immediate relatives (brother, sister, mother, father,
son or daughter) of people who have Parkinson's disease were found to at
increased risk for developing depression and anxiety disorders. The risk
is particularly increased in families
of patients who develop Parkinson's disease before age 75. The authors
emphasizes that the familial susceptibility factors may be genetic,
environmental or a combination of the two, and that further research is
needed to determine their exact nature.
For more information go to the
 The Roman,
Aulus
Cornelius Celsus (c25BC-c50AD), although apparently not a physician
himself, compiled an encyclopedia entitled De artibus (25AD-35AD) that
included De medicina octo libri (The Eight Books of Medicine).
He advised
against administering those who suffered tremor of the sinews with emetics
or drugs that promoted urination, and also against baths and dry sweating.
Relief from worry, rubbing of the limbs and their exercise by ball games
and walking were indicated. The patient could eat whatever he wanted, but
sexual activity should be restricted. If he should succumb, he should
afterwards be rubbed in bed with olive oil, by boys, not men. Fine
tremor was distinguished from a coarser shaking, which was independent of
voluntary motion. So it resembled resting tremor. It could be alleviated
by the application of heat and by bloodletting.
The Roman,
Aulus
Cornelius Celsus (c25BC-c50AD), although apparently not a physician
himself, compiled an encyclopedia entitled De artibus (25AD-35AD) that
included De medicina octo libri (The Eight Books of Medicine).
He advised
against administering those who suffered tremor of the sinews with emetics
or drugs that promoted urination, and also against baths and dry sweating.
Relief from worry, rubbing of the limbs and their exercise by ball games
and walking were indicated. The patient could eat whatever he wanted, but
sexual activity should be restricted. If he should succumb, he should
afterwards be rubbed in bed with olive oil, by boys, not men. Fine
tremor was distinguished from a coarser shaking, which was independent of
voluntary motion. So it resembled resting tremor. It could be alleviated
by the application of heat and by bloodletting.  It is
suggested that selective activation of
mGluR4 is one way to do this and could correct the circuitry that
modulates motor excitability. Published research suggests that mGluR4
activators could work via two distinct mechanisms to alleviate symptoms of
Parkinson's disease.
For more information go to the
It is
suggested that selective activation of
mGluR4 is one way to do this and could correct the circuitry that
modulates motor excitability. Published research suggests that mGluR4
activators could work via two distinct mechanisms to alleviate symptoms of
Parkinson's disease.
For more information go to the
 While patients and
families are aware of the physical challenges that accompany Parkinson�s
disease, few are prepared for the common behavioral issues that impact
their quality of life, including depression, anxiety, dementia, paranoid
delusions, and sleep disorders.
"Making the Connection Between Brain
and Behavior : Coping with Parkinson's Disease",
the only one of its kind, focuses entirely on an area that most doctors
overlook. Written in layman�s terms, it helps readers understand and cope
with a wide variety of Parkinson�s-related behavioral issues and offers
guidance on communicating with the healthcare team.
While patients and
families are aware of the physical challenges that accompany Parkinson�s
disease, few are prepared for the common behavioral issues that impact
their quality of life, including depression, anxiety, dementia, paranoid
delusions, and sleep disorders.
"Making the Connection Between Brain
and Behavior : Coping with Parkinson's Disease",
the only one of its kind, focuses entirely on an area that most doctors
overlook. Written in layman�s terms, it helps readers understand and cope
with a wide variety of Parkinson�s-related behavioral issues and offers
guidance on communicating with the healthcare team.
 She donated her body to science. So after her death an autopsy was carried
out.
There was no sign at all of dementia or Alzheimer's
disease. Several similar non-demented cases aged 85-105 years have
been reported previously, who had neurofibrillary tangles in the medial
temporal lobe, but no deposition of amyloid plaques. Critical questions
raised by the present study include what factors allowed her to be completely
free of dementia despite being 115 years old. Hendrikje van Andel-Schipper had stated that
the secret of her health was a serving of herring every day and drinking
orange juice. She also drank Advocaat (an egg liqueur).
She donated her body to science. So after her death an autopsy was carried
out.
There was no sign at all of dementia or Alzheimer's
disease. Several similar non-demented cases aged 85-105 years have
been reported previously, who had neurofibrillary tangles in the medial
temporal lobe, but no deposition of amyloid plaques. Critical questions
raised by the present study include what factors allowed her to be completely
free of dementia despite being 115 years old. Hendrikje van Andel-Schipper had stated that
the secret of her health was a serving of herring every day and drinking
orange juice. She also drank Advocaat (an egg liqueur).  Parkinson's Disease has long been associated with stoic and inflexible
personality traits. However, although many features of
personality have been studied in Parkinson's
Disease, a systematic study of anger trait and anger
expression
has not been carried out. In this study,
researchers claimed to have found that people with Parkinson's Disease were less
prone to anger than other people, and that they kept more control over the
display of their anger. However, when all of the results are analysed in detail,
the statistical differences are only marginal. What the results instead show is
that people with Parkinson's Disease, despite being claimed to be stoic, are no
less prone to anger than anyone else, and that they are no less ready to
display it.
Parkinson's Disease has long been associated with stoic and inflexible
personality traits. However, although many features of
personality have been studied in Parkinson's
Disease, a systematic study of anger trait and anger
expression
has not been carried out. In this study,
researchers claimed to have found that people with Parkinson's Disease were less
prone to anger than other people, and that they kept more control over the
display of their anger. However, when all of the results are analysed in detail,
the statistical differences are only marginal. What the results instead show is
that people with Parkinson's Disease, despite being claimed to be stoic, are no
less prone to anger than anyone else, and that they are no less ready to
display it.