28th February 2014 - New research
CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE
JAMA Neurology [2014]
Feb 24 [Epub ahead of print] (A.Videnovic, C.Noble, K.J.Reid, J.Peng,
F.W.Turek, A.Marconi, A.W.Rademaker, T.Simuni, C.Zadikoff, P.C.Zee)
Complete abstract
Diurnal fluctuations of Parkinson's Disease symptoms and a high prevalence
of sleep-wake disturbances in Parkinson Disease suggest that the circadian
rhythm is affecting these symptoms. The circadian rhythm is a roughly 24
hour cycle that regulates physiological processes by various factors such as
daylight. Secretion of melatonin from the pineal gland is largely
responsible for this regulation. For more information go to
Circadian rhythms
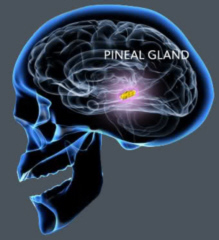 People
with Parkinson's Disease have been found to have blunted circadian rhythms.
The differences and the range of secretion of melatonin from the pineal
gland were found to be lower in Parkinson's Disease than in people that do
not have Parkinson's Disease. Compared with people who had Parkinson's
Disease who did not have excessive daytime sleepiness, people with excessive
daytime sleepiness had narrower ranges of melatonin secretion. Overall
Parkinson's Disease symptoms and duration of symptoms were not significantly
related to the circadian rhythm. So it was only daytime sleepiness and not
Parkinson's Disease symptoms generally that can be affected by the blunted
circadian rhythm that can occur in Parkinson's Disease.
In order to refer to this article on its own
click here.
People
with Parkinson's Disease have been found to have blunted circadian rhythms.
The differences and the range of secretion of melatonin from the pineal
gland were found to be lower in Parkinson's Disease than in people that do
not have Parkinson's Disease. Compared with people who had Parkinson's
Disease who did not have excessive daytime sleepiness, people with excessive
daytime sleepiness had narrower ranges of melatonin secretion. Overall
Parkinson's Disease symptoms and duration of symptoms were not significantly
related to the circadian rhythm. So it was only daytime sleepiness and not
Parkinson's Disease symptoms generally that can be affected by the blunted
circadian rhythm that can occur in Parkinson's Disease.
In order to refer to this article on its own
click here.
|
FOR A
PRINTABLE OR WHITE BACKGROUND VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE
CLICK HERE |
27th February 2014 - History
EARTHWORMS AND OIL OF WINGED ANTS FOR PARKINSON'S DISEASE
 Nicholas
Culpeper (1616-1654) was an English botanist, herbalist, physician and
astrologer. He published books, The English Physitian (1652) and the
Complete Herbal (1653). The Complete Herbal contains both pharmaceutical
and herbal
knowledge. Among the recommendations in Complete Herbal, he suggests sage
for "sinews, troubled with palsy and cramp". For centuries prior to this,
Sage had also been recommended for tremor in the hands. Amongst other
plant remedies Culpepper suggested for palsy and trembling were
bilberries, briony (called "English mandrake"), and mistletoe. In the 1696
edition of his
Pharmacopoeia Londinensis, a variety
of substances were claimed to be useful
in the
treatment of "palsies", the "dead
palsy", and "tremblings". These included "oil of winged ants" and
preparations including earthworms.
For more concerning the history of Parkinson's Disease go to the
History of Parkinson's Disease.
Nicholas
Culpeper (1616-1654) was an English botanist, herbalist, physician and
astrologer. He published books, The English Physitian (1652) and the
Complete Herbal (1653). The Complete Herbal contains both pharmaceutical
and herbal
knowledge. Among the recommendations in Complete Herbal, he suggests sage
for "sinews, troubled with palsy and cramp". For centuries prior to this,
Sage had also been recommended for tremor in the hands. Amongst other
plant remedies Culpepper suggested for palsy and trembling were
bilberries, briony (called "English mandrake"), and mistletoe. In the 1696
edition of his
Pharmacopoeia Londinensis, a variety
of substances were claimed to be useful
in the
treatment of "palsies", the "dead
palsy", and "tremblings". These included "oil of winged ants" and
preparations including earthworms.
For more concerning the history of Parkinson's Disease go to the
History of Parkinson's Disease.
|
FOR A
PRINTABLE OR WHITE BACKGROUND VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE
CLICK HERE |
12th February 2014 - New research
HEARING LOSS IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE
European Journal of Neurology
[2014] Feb 10 [Epub ahead of print] (S.W.Lai, K.F.Liao, C.L.Lin, C.C.Lin,
F.C.Sung)
Complete abstract
Hearing loss has been found to be three times more likely in elderly
people who have Parkinson's Disease. This is partly due to the increased
prevalence of loss of hearing with age. However, hearing loss is still 1.77 times more
likely in elderly people with Parkinson's Disease than it is in elderly people who do not have Parkinson's Disease.
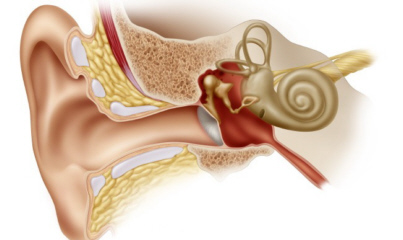 Hearing
is perceived in the Cochlea, in the Organ of Corti, which is the sensory
organ of hearing. For more information go to
Cochlea. Dopamine, whose deficiency causes Parkinson's Disease,
helps to protect against
noise exposure in the Cochlea
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]. Insufficient dopamine can therefore
lead to damage that can result in loss of hearing.
The
cause of the increased likelihood of loss of hearing that can occur in
Parkinson's Disease is therefore originally probably biochemical rather than
structural.
In order to refer to this article on its own
click here.
Hearing
is perceived in the Cochlea, in the Organ of Corti, which is the sensory
organ of hearing. For more information go to
Cochlea. Dopamine, whose deficiency causes Parkinson's Disease,
helps to protect against
noise exposure in the Cochlea
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]. Insufficient dopamine can therefore
lead to damage that can result in loss of hearing.
The
cause of the increased likelihood of loss of hearing that can occur in
Parkinson's Disease is therefore originally probably biochemical rather than
structural.
In order to refer to this article on its own
click here.
|
FOR A
PRINTABLE OR WHITE BACKGROUND VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE
CLICK HERE |
11th February 2014 - New book
PIONEERS OF RECOVERY : HOW PEOPLE WITH PARKINSON'S DISEASE REVERSE THEIR
SYMPTOMS
Robert Rodgers
 Publisher's
description : Parkinsons Recovery Radio show guests often talk about how they
reversed the symptoms of Parkinsons Disease. Now you can read nine of these
amazing stories as they were first told on the radio show in this 2012 release
of Pioneers of Recovery. Each chapter includes details on the steps that each
pioneer took to make miracle of healing happen. Therapies that paved the road to
recovery include : TMJ adjustments, Candida cleanses, Voice Profiling, sound
therapy, Tai Chi, Martial Arts, Qigong, Low Dose Naltrexone, forced exercise,
Chinese medicine, supplements, diet, detoxes. You will be intrigued by how each
pioneer went about reversing their symptoms
Click here for more details. For
more books concerning Parkinson's Disease go to
Parkinson's Disease Books
Publisher's
description : Parkinsons Recovery Radio show guests often talk about how they
reversed the symptoms of Parkinsons Disease. Now you can read nine of these
amazing stories as they were first told on the radio show in this 2012 release
of Pioneers of Recovery. Each chapter includes details on the steps that each
pioneer took to make miracle of healing happen. Therapies that paved the road to
recovery include : TMJ adjustments, Candida cleanses, Voice Profiling, sound
therapy, Tai Chi, Martial Arts, Qigong, Low Dose Naltrexone, forced exercise,
Chinese medicine, supplements, diet, detoxes. You will be intrigued by how each
pioneer went about reversing their symptoms
Click here for more details. For
more books concerning Parkinson's Disease go to
Parkinson's Disease Books
|
FOR A
PRINTABLE OR WHITE BACKGROUND VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE
CLICK HERE |
8th February 2014 - New review
SKIN DISORDERS IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE
The integumentary system is the
skin and its associated glands, including the sweat glands, the sebaceous
glands, and the
hair and nails. Those medical disorders asociated with the skin that
commonly occur in Parkinson's Disease are seborrhea, hyperhidrosis, and
melanoma.
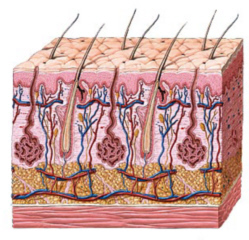 Seborrhea
causes excessively oily skin. Sebaceous glands are glands in the skin that
secrete sebum, to lubricate the skin and hair. Seborrhea can therefore
result in excessive secretion of sebum by the sebaceous glands and its
accumulation on the skin surface. There is an increased likelihood of
seborrhea in Parkinson's Disease that is due to low dopamine. For more
information go to
Seborrhea
Seborrhea
causes excessively oily skin. Sebaceous glands are glands in the skin that
secrete sebum, to lubricate the skin and hair. Seborrhea can therefore
result in excessive secretion of sebum by the sebaceous glands and its
accumulation on the skin surface. There is an increased likelihood of
seborrhea in Parkinson's Disease that is due to low dopamine. For more
information go to
Seborrhea
Hyperhidrosis is
overactive sweat glands. Hyperhidrosis can therefore result in excessive
sweat secretion. There is an increased likelihood of hyperhidrosis in
Parkinson's Disease. Instead of being due to Parkinson's Disease, the
increased sweat secretion is usually due to Parkinson's Disease drugs. As an
unintended side effect L-dopa can produce adrenaline, which stimulates the
sweat glands. For more information
go to
Hyperhidrosis
Melanoma is a
form of skin cancer. The risk of melanoma could sometimes be as much as four
to five times higher in Parkinson's Disease. The melanocyes in the skin
produce melanin, which is made from L-tyrosine via L-dopa. This is the same
means as dopamine in the dopaminergic neurons. Given that melanin helps to
protect skin cells from Ultra Violet induced damage, melanoma is probably
increased in Parkinson's Disease because of the reduced capacity to produce
L-dopa in the melanocytes. For more information
go to
Melanoma In order to refer to this article on its own
click here.
|
FOR A
PRINTABLE OR WHITE BACKGROUND VERSION OF THIS ARTICLE
CLICK HERE |
.gif)
.gif)
 People
with Parkinson's Disease have been found to have blunted circadian rhythms.
The differences and the range of secretion of melatonin from the pineal
gland were found to be lower in Parkinson's Disease than in people that do
not have Parkinson's Disease. Compared with people who had Parkinson's
Disease who did not have excessive daytime sleepiness, people with excessive
daytime sleepiness had narrower ranges of melatonin secretion. Overall
Parkinson's Disease symptoms and duration of symptoms were not significantly
related to the circadian rhythm. So it was only daytime sleepiness and not
Parkinson's Disease symptoms generally that can be affected by the blunted
circadian rhythm that can occur in Parkinson's Disease.
In order to refer to this article on its own
People
with Parkinson's Disease have been found to have blunted circadian rhythms.
The differences and the range of secretion of melatonin from the pineal
gland were found to be lower in Parkinson's Disease than in people that do
not have Parkinson's Disease. Compared with people who had Parkinson's
Disease who did not have excessive daytime sleepiness, people with excessive
daytime sleepiness had narrower ranges of melatonin secretion. Overall
Parkinson's Disease symptoms and duration of symptoms were not significantly
related to the circadian rhythm. So it was only daytime sleepiness and not
Parkinson's Disease symptoms generally that can be affected by the blunted
circadian rhythm that can occur in Parkinson's Disease.
In order to refer to this article on its own
 Nicholas
Culpeper (1616-1654) was an English botanist, herbalist, physician and
astrologer. He published books, The English Physitian (1652) and the
Complete Herbal (1653). The Complete Herbal contains both pharmaceutical
and herbal
knowledge. Among the recommendations in Complete Herbal, he suggests sage
for "sinews, troubled with palsy and cramp". For centuries prior to this,
Sage had also been recommended for tremor in the hands. Amongst other
plant remedies Culpepper suggested for palsy and trembling were
bilberries, briony (called "English mandrake"), and mistletoe. In the 1696
edition of his
Nicholas
Culpeper (1616-1654) was an English botanist, herbalist, physician and
astrologer. He published books, The English Physitian (1652) and the
Complete Herbal (1653). The Complete Herbal contains both pharmaceutical
and herbal
knowledge. Among the recommendations in Complete Herbal, he suggests sage
for "sinews, troubled with palsy and cramp". For centuries prior to this,
Sage had also been recommended for tremor in the hands. Amongst other
plant remedies Culpepper suggested for palsy and trembling were
bilberries, briony (called "English mandrake"), and mistletoe. In the 1696
edition of his 
 Publisher's
description : Parkinsons Recovery Radio show guests often talk about how they
reversed the symptoms of Parkinsons Disease. Now you can read nine of these
amazing stories as they were first told on the radio show in this 2012 release
of Pioneers of Recovery. Each chapter includes details on the steps that each
pioneer took to make miracle of healing happen. Therapies that paved the road to
recovery include : TMJ adjustments, Candida cleanses, Voice Profiling, sound
therapy, Tai Chi, Martial Arts, Qigong, Low Dose Naltrexone, forced exercise,
Chinese medicine, supplements, diet, detoxes. You will be intrigued by how each
pioneer went about reversing their symptoms
Publisher's
description : Parkinsons Recovery Radio show guests often talk about how they
reversed the symptoms of Parkinsons Disease. Now you can read nine of these
amazing stories as they were first told on the radio show in this 2012 release
of Pioneers of Recovery. Each chapter includes details on the steps that each
pioneer took to make miracle of healing happen. Therapies that paved the road to
recovery include : TMJ adjustments, Candida cleanses, Voice Profiling, sound
therapy, Tai Chi, Martial Arts, Qigong, Low Dose Naltrexone, forced exercise,
Chinese medicine, supplements, diet, detoxes. You will be intrigued by how each
pioneer went about reversing their symptoms
 Seborrhea
causes excessively oily skin. Sebaceous glands are glands in the skin that
secrete sebum, to lubricate the skin and hair. Seborrhea can therefore
result in excessive secretion of sebum by the sebaceous glands and its
accumulation on the skin surface. There is an increased likelihood of
seborrhea in Parkinson's Disease that is due to low dopamine. For more
information go to
Seborrhea
causes excessively oily skin. Sebaceous glands are glands in the skin that
secrete sebum, to lubricate the skin and hair. Seborrhea can therefore
result in excessive secretion of sebum by the sebaceous glands and its
accumulation on the skin surface. There is an increased likelihood of
seborrhea in Parkinson's Disease that is due to low dopamine. For more
information go to